Understanding SAP Intelligent Robotic Process Automation (RPA)
Robots entered industrial processes to automate activities more than a decade ago. Computerising the manual process was considered as automation until recently. Now it is time for Robots to enter the computerized processes to relieve repetitive human efforts involved.

SAP is a process-centric solution. Even in this, manual tasks which are repetitive & high volume, continue to exist and SAP has brought in “Intelligent Robotic Process Automation (RPA)” as a solution to mitigate this challenge. Many times, such manual tasks are repeatedly performed by different groups of people, also in different systems at times, within an organisation. This blog outlines RPA, at a high level, to enable any SAP Consultant to get an understanding of this solution.
RPA consists of “Bots”, designed and created by an SAP Consultant or an “expert user” for performing certain repetitive tasks in a chosen process. “Bots” can work as a “Digital Assistant” to the user which are classified as “Attended Bots”. Bots can also work in an “unattended mode”, just as a “Digital Worker”, to perform certain tasks in the background. These Bots can be orchestrated and monitored from a supervisor console. This is explained graphically below in Exhibit-1.
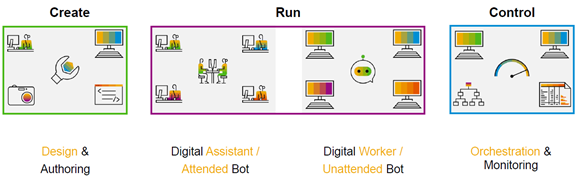
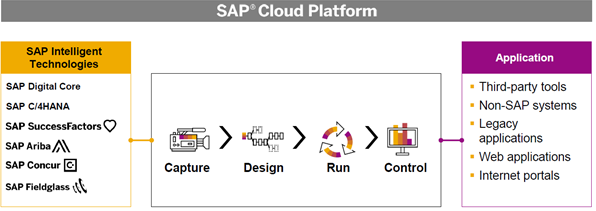
SAP Intelligent RPA is a single unified Cloud based solution. It includes “on-premise” automation tools as well. This is an end-to-end solution to automate steps. Most of us are familiar with “Macros and VBA Scripts” to automate certain tasks in Microsoft (MS) applications such as Excel. However, it can work only within the single application and cannot work across other Non-MS applications. This is where RPA overcomes such limitations. It can work with Non-SAP Systems and Legacy applications, as well as SAP’s solutions such as SAP Digital Core, Ariba, Concur etc…. In addition, RPA does not need any programming skills to build a “Bot”. See exhibit-2 below to understand, how RPA integrates seamlessly across solutions.
SAP Intelligent RPA has three components as mentioned below. Let’s look at them in detail in the following sections:
- Desktop Agent
- Cloud Factory
- Desktop Studio
Desktop Agent-
This component is installed by a cloud administrator in an end user’s computer. Once installed, the administrator privileges are not required by the Agent on the machine. The Agent will adopt the user profile and its Windows credentials for operations.
Cloud Factory–
Cloud Factory is a dedicated Bot Management Central component that orchestrates all process automations. It monitors and controls jobs and agents in the landscape and presents them in the form of a dashboard. It consists of three different sub-components named Hierarchies, Environments, Packages and Configurations.
Desktop Studio
Desktop Studio is the component (we will go into more detail later in where the bots are developed. The desktop studio combines all the relevant information of a bot and delivers what is known as the “package”. This package needs to be imported into Cloud Factory.
Summary:
SAP Intelligent RPA is a very interesting tool. SAP has articulated a great roadmap ahead for Intelligent RPA. RPA creates a layer that sits on top of existing systems and processes without having a need to rewrite thousands of lines of codes. The automation covers end-to-end steps of the process, spanning across a multitude of systems, including SAP and Non-SAP solutions. These create great advantages for every organization. Any organisation can spend minimal amounts of time to review the existing processes and come up with areas of optimization using RPA. It is really a great opportunity for any SAP consultant to review and produce RPA implementations in many areas and it will add great value to every customer.


