AI is seamlessly integrated into the core of enterprise resource planning (ERP) frameworks. These crucial AI and ERP software applications facilitate the management and connection of daily business processes in finance, operations, HR, and customer service. Designed for data integration, automation, and reporting across diverse functions, ERP systems now harness the power of AI to enhance their capabilities.
However, as business operations become more intricate and dynamic, regular AI and ERP frameworks will likely be unable to keep up with the changing requirements and expectations of clients, employees, and partners. This is where artificial intelligence (AI) comes in. AI is the capacity of computers to perform tasks that require intelligence, like learning, reasoning, and guidance. AI can improve AI and ERP frameworks by providing advanced analysis, forecasting, automation, personalization, and optimization.
In this article, we will investigate a portion of simulated intelligence’s advantages and use cases in ERP Systems and how they can assist with further developing plans of action and results.
Chat GPT: The Power of Artificial Intelligence in Conversational Interfaces
Benefits of AI in ERP Systems
Simulated intelligence can carry many advantages to ERP frameworks, for example,
- Further developed effectiveness and efficiency: simulated intelligence can computerize monotonous and drawn-out undertakings that would somehow require human mediation, for example, information section, receipt handling, stock administration, and finance. This can save time and assets, diminish blunders and extortion, and increment precision and consistence.
- Upgraded bits of knowledge and navigation: artificial intelligence can examine enormous volumes of information from different sources and give noteworthy experiences that can assist with further developing business execution, consumer loyalty, and productivity. Artificial intelligence can likewise create figures and suggestions in light of verifiable information and current circumstances, empowering better preparation and enhancement of assets, cycles, and techniques.
- Expanded readiness and advancement: artificial intelligence can empower ERP frameworks to adjust to changing business conditions and client requests by gaining from information and input. Computer based intelligence can likewise assist with distinguishing new open doors and patterns, make new items and administrations, and further develop client experience and faithfulness.
- Diminished expenses and dangers: computer based intelligence can assist with upgrading ERP frameworks by decreasing waste, margin time, support, and functional expenses. Computer based intelligence can likewise assist with alleviating gambles by recognizing inconsistencies, dangers, and weaknesses, and giving cautions and arrangements.
Use Cases of AI in ERP Systems
Man-made intelligence can be applied to different parts of ERP frameworks to upgrade their usefulness and worth. A portion of the normal use cases are:
- Progressed investigation and determining: simulated intelligence can assist with further developing expectations and projections for different tasks exercises, for example, store network the board, creation arranging, stock administration, deals guaging, and so on. Simulated intelligence can utilize authentic information and current circumstances to produce exact and solid figures that can assist with enhancing asset portion, request the executives, stock recharging, and so on. For instance, Samsung involves computer based intelligence for better interest guaging.
- HR the board: man-made intelligence can help robotize and further develop different HR errands like enrollment, execution the executives, remuneration the executives, worker commitment, and so forth. Computer based intelligence can utilize regular language handling (NLP) to dissect resumes, meetings, input, and reviews, and give bits of knowledge on competitors’ abilities, characters, and fit for the gig. Man-made intelligence can likewise utilize AI (ML) to screen representative execution, efficiency, and fulfillment, and give customized instructing, preparing, and compensates. For instance, Vodafone utilizes simulated intelligence to offer insightful client care.
- Finance/bookkeeping the executives: computer based intelligence can help robotize and work on different money/bookkeeping capabilities, for example, exchange handling, receipt handling, monetary examination, announcing, and so on. Artificial intelligence can utilize optical person acknowledgment (OCR) to extricate information from records and solicitations and approve and accommodate them with different sources. Man-made intelligence can likewise utilize ML and NLP to investigate monetary information and give bits of knowledge on income, benefit, risk, and so on. For instance, AmerisourceBergen utilizes simulated intelligence to decide creation costs.
- Client support the executives: simulated intelligence can help give quicker, less expensive, and more reliable client assistance by utilizing chatbots and remote helpers that can answer normal questions and demands utilizing NLP and regular language age (NLG). Simulated intelligence can likewise utilize ML and NLP to investigate client input and feeling and give customized suggestions and arrangements. For instance, Vodafone utilizes computer based intelligence to offer keen client support.
Dangers and Difficulties of simulated intelligence in ERP Frameworks: While computer based intelligence can carry many advantages to ERP frameworks, it can likewise present new dangers and provokes that should be tended to and made due. A portion of the normal dangers and difficulties are:
- Information protection and security: computer based intelligence depends on a lot of information to learn and perform undertakings. Nonetheless, this information might contain delicate or individual data that should be safeguarded from unapproved access, use, or divulgence. Information security and security guidelines, like the Overall Information Insurance Guideline (GDPR), may force severe necessities on how information is gathered, put away, handled, and shared. Simulated intelligence frameworks need to conform to these guidelines and guarantee that information is scrambled, anonymized, or pseudonymized when vital. Artificial intelligence frameworks additionally need to forestall information breaks, holes, or robberies that could think twice about trustworthiness and privacy.
- Straightforwardness and reasonableness: computer based intelligence frameworks frequently work as secret elements, implying that their inward activities and rationale are not effectively justifiable or interpretable by people. This can present difficulties for trust, responsibility, and consistence. For instance, on the off chance that a man-made intelligence framework goes with a choice or proposal that influences a client, a representative, or a partner, how might it make sense of the reasoning behind it? How might it legitimize its activities assuming they are tested or questioned? How might it guarantee that it follows moral standards and lawful standards? Straightforwardness and logic are fundamental for building trust and trust in simulated intelligence frameworks and guaranteeing that they are fair, precise, and solid.
- Predisposition and decency: man-made intelligence frameworks might acquire or enhance inclinations from the information they use or the calculations they utilize. These predispositions might bring about out of line or prejudicial results for specific gatherings or people. For instance, an artificial intelligence framework that predicts financial assessments or advance endorsements might lean toward specific socioeconomics over others in view of verifiable information or presumptions. Predisposition and reasonableness are significant for guaranteeing that man-made intelligence frameworks don’t damage or hindrance anybody in view of their qualities or inclinations. Artificial intelligence frameworks should be evaluated and observed for likely inclinations and adjusted or relieved when fundamental.
- Network protection and strength: computer based intelligence frameworks might be powerless against cyberattacks or vindictive control by outer or inward entertainers. These assaults might expect to take, bad, or obliterate information; modify or disrupt framework usefulness; or impact framework conduct or results. For instance, an aggressor might infuse bogus or deluding information into a computer based intelligence framework to think twice about precision or dependability; separate private data from a computer based intelligence framework by figuring out its models; or take advantage of weaknesses in an artificial intelligence framework to acquire unapproved access or control. Network safety and strength are basic for guaranteeing that simulated intelligence frameworks are safeguarded from digital dangers and can recuperate from interruptions or harms.
- All in all, computer based intelligence and ERP frameworks can cooperate to further develop business proficiency, adequacy, and advancement. Computer based intelligence can improve ERP frameworks by giving high level investigation, guaging, robotization, personalization, and streamlining. Man-made intelligence can likewise assist with working on different parts of ERP frameworks like HR the board, finance/bookkeeping the executives, and client care the board. In any case, computer based intelligence additionally presents new dangers.
Likewise with any innovation project care should be taken to guarantee reception matches business objectives. All things considered, I like to say, innovation won’t take care of your concern. It basically intensifies anything that you apply it to.
AI can improve ERP systems by adding new capabilities, such as
Advanced analytics and forecasting: computer based intelligence can utilize authentic information and current circumstances to make expectations and proposals for different tasks exercises, for example, creation arranging, stock administration, request estimating, and deals execution. Simulated intelligence can likewise assist with recognizing examples, patterns, and irregularities in information, and give clarifications and ideas to progress.
HR: artificial intelligence can help computerize and advance HR capabilities, like enrollment, execution the executives, pay the board, and representative commitment. Simulated intelligence can likewise help customize and fit HR administrations to individual representatives’ necessities and inclinations, like vocation improvement, learning open doors, and criticism.
Finance/bookkeeping: artificial intelligence can help computerize and smooth out bookkeeping capabilities, for example, exchange handling, proclamation confirmation, report age, and review consistence. Simulated intelligence can likewise assist with working on monetary administration by giving bits of knowledge into income, working capital, productivity, and hazard.
Client care: computer based intelligence can help give quicker, less expensive, and more steady assistance to clients by utilizing chatbots, voice collaborators, or other conversational man-made intelligence frameworks to address normal requests, resolve issues, or give data. Man-made intelligence can likewise help customize and alter client collaborations by utilizing information examination, regular language handling (NLP), and opinion investigation.
There are numerous ERP systems that utilization AI intelligence to offer these advantages to their clients. Here are a few instances of computer based intelligence empowered ERP arrangements:
Oracle AI Apps for Oracle Financials: This set-up of simulated intelligence controlled applications helps money and acquisition groups further develop execution, enhance working capital, and increment computerization across payables, receivables, acquirement, and provider the executives. For instance, the Dynamic Limiting element utilizes man-made intelligence to make a limiting project that is customized to every individual provider in view of their profile, spend information, and installment conduct.
SAP Leonardo: This is an assortment of microservices that coordinate with SAP’s cloud stage to empower clients to use man-made intelligence advancements, for example, AI (ML), NLP, and PC vision in their ERP processes. For instance, the Interest Driven Recharging highlight utilizes ML to upgrade stock levels in view of genuine client interest.
Infor: This is a cloud-based ERP framework that takes care of a large number of ventures, like assembling, medical services, and retail. It utilizes artificial intelligence to give industry-explicit arrangements and experiences. For instance, the Infor Coleman man-made intelligence Stage utilizes NLP, picture acknowledgment, and ML to robotize undertakings, give suggestions, and produce reports.
What is AI integrated ERP ?
Britannica characterizes artificial intelligence (AI) as the “capacity of an advanced PC or PC controlled robot to perform undertakings generally related” with people. Utilization of man-made consciousness programming and methods to ERP arrangements is known as artificial intelligence in ERP. Intelligent chatbots, wise cycle computerization, and computer based intelligence upgraded monetary arranging are instances of simulated intelligence devices used in ERP programming. ERP frameworks with computer based intelligence capacities work to impact an organization’s everyday cycles and tasks. Organizations can increment efficiency while upgrading human abilities by smoothing out routine cycles, disposing of human mistake, and reducing working expenses. A large number of organization capabilities, including bookkeeping, examination, information mining, deals robotization, and distribution center administration, can profit from the use of simulated intelligence in ERP frameworks.
What are the current technology trends, and what does the future hold for this digital transformation?
There are forecasts that the AI ERP market would grow by about $190 billion by 2025, as per a market study. It’s the ideal opportunity for organizations to refresh to the most current ERP framework tasks and cycles on the grounds that computerized change is an arising element of another time. While ML rebuilds the business climate by presenting development and robotization, artificial intelligence makes task the board more straightforward. The rise of the freshest ERP arrangements embodies the functional productivity that computer based intelligence and ML will be expected to accomplish sooner rather than later.
How does Artificial intelligence and ML enhance ERP ?
To acquire an upper hand, organizations are depending on wise innovations and computerized reasoning. Savvy assembling and AI are as of now helping organizations to increment efficiency, for example concerning money and client the board. How about we look at what artificial intelligence will mean for ERP frameworks in these three regions.
1.Information dealing with and business insight: Figuring out the developing volume of information is one of the fundamental issues we notice. With such a lot of data about clients, their way of behaving, and the association’s cycles, it’s challenging to keep awake and get pertinent bits of knowledge from it. With artificial intelligence and ML coordinated into your cloud ERP programming, you will actually want to include information to solid simulated intelligence calculations. You can then recognize patterns in your cycle and activities that probably won’t be obvious in any case.
2.Process Mechanization: Robotizing business processes assists you with setting aside both time and cash. There are a few obligations that are performed frequently and monotonously in each business. Such normal cycles can be computerized utilizing AI. Moreover, this assists you with saving a ton of time, cash, and HR. With computer based intelligence and ML worked in your ERP and fabricating programming, you can guide your HR to more delicate and high-need occupations.
3.Client experience: Directing client associations with clients is made more straightforward by incorporating man-made intelligence or ML into any organization’s ERP. Using client information gives knowledge into request inventory network elements and grasps purchasing patterns. High level man-made intelligence calculations joined with ERP help in observing client ways of behaving, estimating how habitually they visit sites, and surveying shopper spending power. Obviously simulated intelligence ERP smoothes out the business processes that further develop client experience and buyer trust. One more benefit of this method is that it very well may be utilized to watch out for the holes, address issues, and immediately fix botches.
4.Better advertising arrangements: ERP combination of computer based intelligence and ML additionally supports the investigation of neglected business open doors. It gives data to the clients about their buying designs, orientation, age, demography, and different elements. Because of ERP frameworks that help computer based intelligence, organizations can now furnish better client support and draw in with an assortment of market gatherings. Many business sectors have been neglected so far, yet the presentation of computer based intelligence has further developed market perceivability and permitted the organization to investigate different conceivable outcomes.
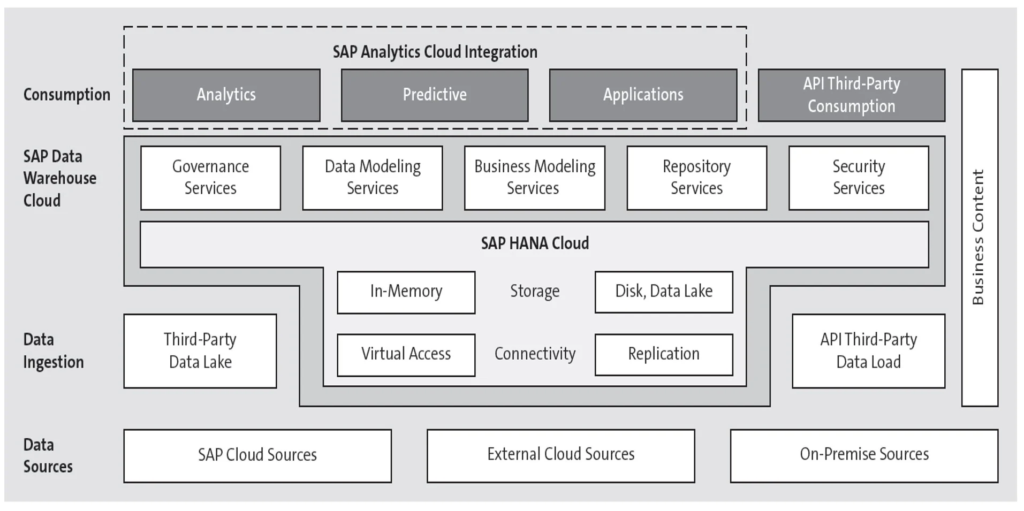
AI And SAP: Beneficial Combination?
What are the benefits of Artificial intelligence integrated ERP to the businesses ?
There are other heap advantages of artificial intelligence fueled ERP programming for business process improvement. Allow us to investigate some of them in the accompanying.
1. Savvy Information Handling : ERP programming is a cunning method for expanding the efficiency and proficiency of your business processes, yet it can’t deal with information at the very supersonic speed that a man-made intelligence empowered framework manages with no human intercession. With the utilization of an artificial intelligence incorporated ERP framework, you might get to constant information from numerous divisions and make the fitting allowances for exact and viable preparation. With practically no or very little human help, it creates exhaustive reports.
2. Coordinated and High level Investigation: computer based intelligence innovation has the ability to deal with tremendous volumes of information. A standard ERP framework can create nitty gritty reports by assessing the verifiable information it has close by, however a simulated intelligence empowered framework goes far further. You might utilize prescient examination to expand the assurance of your choices. This further develops your business deftness while empowering you to move toward issues from each point.
3. Further developed Precision in Estimating: Man-made brainpower and AI are acquiring offer as promising advancements for working on figure exactness. ERP frameworks with artificial intelligence abilities help organizations in upgrading their anticipating systems. These product arrangements are made to close the hole among anticipated and genuine necessities, from assessing business requests and staffing prerequisites to income and other basic exercises.
4. Supporting Mechanization: Manual information section can bring about huge responsibilities for your representatives, costing you many worker hours and being inclined to mistakes. By consolidating an ERP framework with man-made intelligence, you can computerize work processes, save time by eliminating the requirement for human communication while transferring information, and work on functional adequacy.
5. Boosting Interaction Effectiveness: The business activities are additionally upgraded by the option of simulated intelligence to your ERP framework. This state of the art ERP arrangement inspects your past information to suggest the most useful cycles or work processes. Business activities are improved, and each work is finished rapidly and without mistakes, bringing about critical time investment funds and more prominent efficiencies.
6. Worked on Admittance to Information: As man-made reasoning turned into a piece of ERP frameworks, organizations started to profit from the capacity to separate data from huge informational indexes and change it into helpful data. This eventually prompted decisions and exercises that are invaluable to the extension of the business.
7. Guaranteeing More noteworthy Readiness: computer based intelligence empowered ERP reception smoothes out business cycles and makes firms more lithe. Because of computer based intelligence mix, routine methods that once consumed a huge part of your representatives’ useful time and caused failures are presently robotized.
8. Create Customized Business Reports: The presentation of computer based intelligence innovation changes how reports are delivered. The coordinated ERP framework can remove corporate information and produce smart reports in the ideal organization for the clients. This kills the requirement for manual information extraction, estimations, and report compromise. Finding explicit data is significantly simpler with computerization, and in particular, detailing quality is improved, enhancing scientific decision-production for corporate development and further developing return for money invested.
Read related blogs:
Machine Learning versus Artificial Intelligence
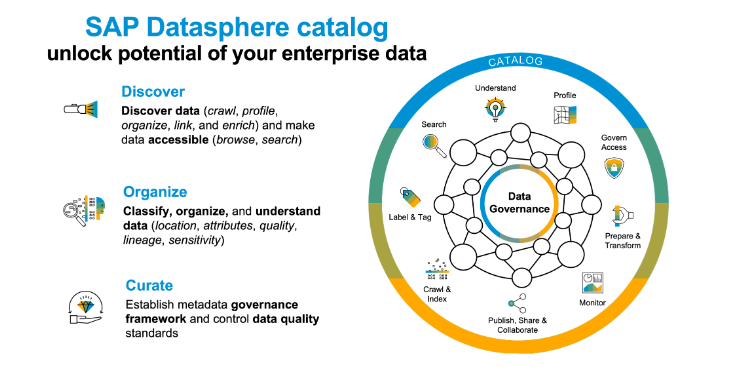
SAP BTP: A to Z of SAP Conversational AI
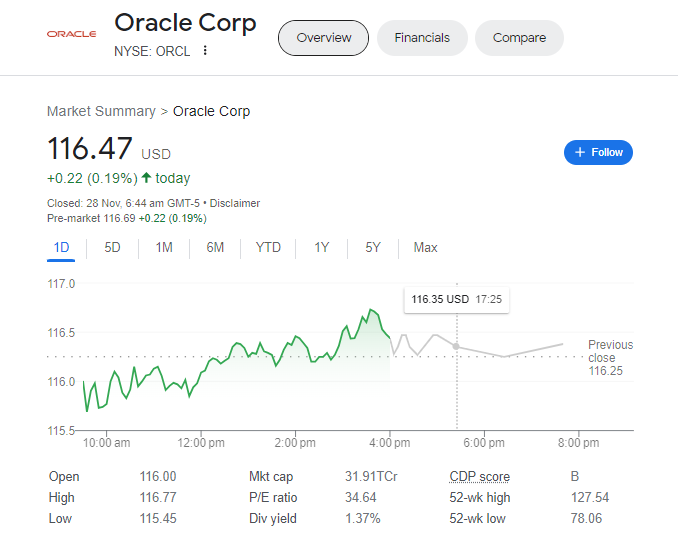
the Power of Oracle Business Intelligence