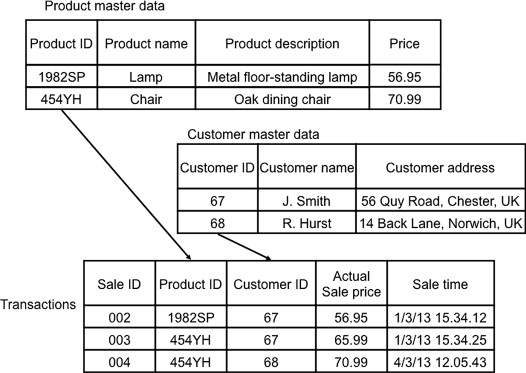
Material description table in sap
Welcome to the world of SAP, where complex business processes are simplified, and data management is made efficient. In this article, we delve into the material description table in SAP, uncovering its importance and functionality.

An Overview of SAP Material Management
The material description table is a critical component within the SAP system, providing a centralized platform to store and manage textual descriptions of materials. Whether it’s a finished product, raw material, or service, having accurate and comprehensive descriptions is vital for streamlined operations and effective decision-making.
Within this table, various attributes such as language, short text, long text, and industry-specific details are stored and associated with specific materials or products. This allows businesses to easily retrieve and utilize these descriptions in various SAP modules, such as sales, procurement, and production.
By maintaining a well-organized material description table, organizations can enhance productivity, ensure data consistency, and improve customer satisfaction. With the ability to customize fields and labels as per business requirements, SAP empowers companies to optimize their material master data management.
So join us as we explore the intricacies of the material description table in SAP, uncovering its significance in maintaining accurate and reliable product information within the SAP ecosystem.
Top 13 Benefits of SAP ERP System for Business
Importance of Material Description Table in SAP
The material description table plays a crucial role in the SAP system, serving as a central repository for all textual descriptions associated with materials. This table ensures that important information about products, such as their characteristics, usage instructions, and technical specifications, is easily accessible and up-to-date.
Having accurate and comprehensive material descriptions is essential for effective decision-making in various business processes. For example, in the procurement module, buyers rely on these descriptions to identify the right materials to source, ensuring that the purchased items meet the required specifications. Similarly, in the sales module, sales representatives rely on material descriptions to provide accurate information to customers, enabling them to make informed purchasing decisions.
Additionally, the material description table allows businesses to maintain consistency across different departments and functions. By centralizing the storage of material descriptions, organizations can avoid duplication and inconsistencies that can arise when different teams maintain their own descriptions. This ensures that everyone within the organization is working with the same set of information, minimizing errors and confusion.
Furthermore, the material description table provides a foundation for analytics and reporting. By having well-structured descriptions stored in a standardized format, businesses can easily extract and analyze data related to specific materials, enabling them to gain valuable insights into their inventory, sales performance, and customer preferences.
In summary, the material description table in SAP is not just a repository for textual information; it is a critical component that supports efficient business processes, improves data consistency, and empowers organizations to make informed decisions.
SAP Big Data: Optimizing The Architecture
Structure and Fields of Material Description Table
The material description table in SAP is structured to capture and store various attributes and details related to materials. Let’s explore the different fields that make up this table and understand their significance.
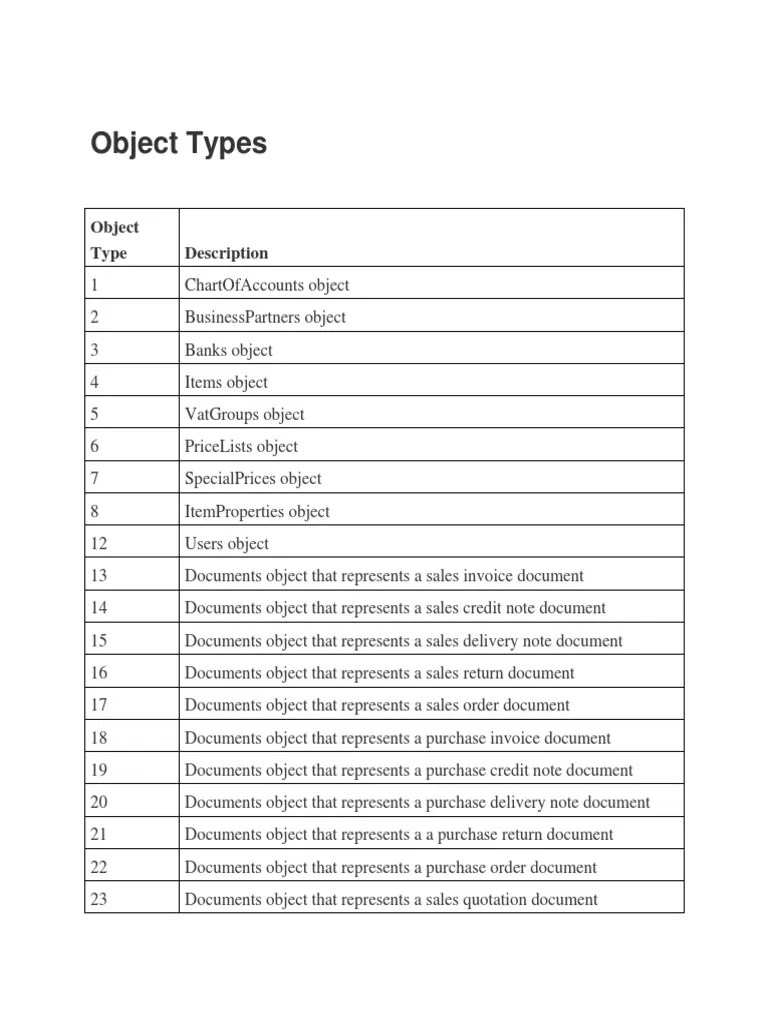
- Material Number: This field serves as the primary key in the material description table. It uniquely identifies each material or product within the SAP system. It is crucial for maintaining data integrity and ensuring accurate retrieval of material descriptions.
- Language: The language field indicates the language in which the material description is written. This allows businesses to store descriptions in multiple languages, catering to their global operations and multilingual customer base.
- Short Text: The short text field is used to store a concise and brief description of the material. It typically provides a high-level overview of the material’s purpose, characteristics, or usage. This field is often used in transactional screens and reports, where space is limited.
- Long Text: The long text field provides a more detailed description of the material. It allows businesses to capture additional information that cannot be accommodated in the short text field. This field is commonly used in master data screens and reports, where more extensive information is required.
- Industry-Specific Details: Depending on the industry or sector in which the organization operates, there may be additional fields in the material description table to capture industry-specific details. For example, in the pharmaceutical industry, fields related to active ingredients, dosage forms, and therapeutic indications may be included.
The structure of the material description table can be customized to align with the specific requirements of each business. SAP provides flexibility in adding custom fields and labels to capture unique information that is relevant to the organization’s products and processes.
Now that we understand the structure and fields of the material description table, let’s explore how to access and view this table in SAP.
How to Access and View Material Description Table in SAP
Accessing and viewing the material description table in SAP is a straightforward process. There are several ways to accomplish this, depending on the user’s role and the SAP module being used. Here are a few common methods:
- Transaction Code: SAP provides transaction codes that allow users to access specific screens or functionalities directly. To view the material description table, one can use transaction code MM03, which is the standard transaction for displaying material master data.
- Navigation Path: Another way to access the material description table is through the SAP menu. Users can navigate to the “Logistics” or “Materials Management” module and select the appropriate options to view material master data. This method is useful for users who are not familiar with transaction codes.
Once the user has accessed the material description table, they can search for a specific material using its material number or any other relevant criteria. The table will display the material’s description and associated details, such as language, short text, and long text.
Users can also customize the display of the material description table to include or exclude specific fields based on their requirements. This flexibility allows users to focus on the information that is most relevant to their tasks and responsibilities.
Now that we know how to access and view the material description table, let’s dive deeper into the significance of material descriptions and how they impact various business processes.
Understanding Material Descriptions and Their Significance
Material descriptions play a crucial role in accurately representing products within the SAP system. They provide essential information about materials, enabling businesses to effectively manage their inventory, sales, and procurement processes. Let’s explore the significance of material descriptions in different areas of the SAP ecosystem.
- Inventory Management: Material descriptions are vital for inventory management, as they enable businesses to identify and differentiate between various materials. Accurate and detailed descriptions help warehouse personnel locate and pick the right items for outbound shipments and ensure that incoming materials are correctly received and stored.
- Sales and Distribution: In the sales module, material descriptions are crucial for sales representatives to provide accurate and comprehensive information to customers. A well-written description can highlight the unique features and benefits of a product, helping sales teams effectively communicate its value proposition.
- Procurement: Material descriptions are essential for procurement teams to identify and source the right materials from suppliers. Detailed descriptions help buyers assess the suitability of materials for their organization’s requirements, ensuring that the purchased items meet the necessary specifications.
- Production Planning: Material descriptions play a significant role in production planning, as they provide essential information about the materials required for manufacturing processes. Accurate descriptions help production planners identify and allocate the necessary resources, ensuring smooth operations and timely delivery of finished goods.
- Reporting and Analytics: Material descriptions are invaluable for reporting and analytics purposes. They allow businesses to generate meaningful insights by analyzing sales performance, inventory levels, and customer preferences based on specific material attributes. Accurate and consistent descriptions enable organizations to make data-driven decisions and identify opportunities for improvement.
In summary, material descriptions are not just textual information; they are a critical element that supports various business processes within the SAP ecosystem. Accurate and comprehensive descriptions enhance operational efficiency, improve customer satisfaction, and enable informed decision-making.
Now that we understand the significance of material descriptions, let’s explore how to update and maintain them in SAP.
Updating Material Descriptions in SAP
Keeping material descriptions up-to-date is essential for maintaining accurate and reliable product information within the SAP system. Here are the steps to update material descriptions in SAP:
- Access the Material Master Data: To update material descriptions, users need to access the material master data screen. This can be done through transaction code MM02 or by navigating through the SAP menu to the appropriate module and options.
- Select the Material: Once in the material master data screen, users can search and select the material for which they want to update the description. This can be done using the material number or any other relevant criteria.
- Update the Descriptions: In the material master data screen, users can navigate to the relevant fields for short text and long text descriptions. They can then modify the existing descriptions or enter new ones as per the required changes. Users can also select the appropriate language for the description if multiple languages are supported.
- Save the Changes: After updating the material descriptions, users need to save the changes to ensure that the updated information is stored in the material description table. The updated descriptions will then be available for use in various SAP modules and processes.
It is important to note that updating material descriptions should be done with care and accuracy. Inaccurate or misleading descriptions can lead to confusion, errors, and inefficiencies in business processes. Therefore, it is recommended to follow established guidelines and quality checks when updating material descriptions.
Now that we know how to update material descriptions, let’s explore some best practices for maintaining the material description table in SAP.
Best Practices for Maintaining Material Description Table
Maintaining the material description table in SAP requires attention to detail and adherence to best practices. Following these practices can help organizations ensure data consistency, improve productivity, and optimize their material master data management. Here are some key best practices to consider:
- Standardize Descriptions: Establishing standard guidelines for material descriptions helps maintain consistency across the organization. This includes guidelines for language usage, terminology, and formatting. Standardization ensures that everyone within the organization understands and interprets material descriptions consistently.
- Regular Updates and Reviews: Material descriptions should be regularly reviewed and updated to reflect any changes in products, specifications, or industry standards. This ensures that the information remains accurate and up-to-date, enabling informed decision-making.
- Quality Checks: Implementing quality checks and validation rules during the update process can help maintain data integrity and prevent errors. These checks can include ensuring the use of approved terminology, validating the length of descriptions, and verifying the accuracy of entered information.
- Training and Documentation: Providing training and documentation to users who update material descriptions can help ensure consistency and accuracy. This includes educating users on the importance of material descriptions, explaining the guidelines for updating them, and offering support resources for any questions or issues that may arise.
- Collaboration and Communication: Effective collaboration and communication between different departments and functions are essential for maintaining the material description table. Regular communication channels should be established to address any discrepancies or changes in material descriptions, ensuring that everyone is aligned and working with the most accurate and updated information.
By following these best practices, organizations can optimize their material description table and ensure the integrity and accuracy of their product information within the SAP system.
Now, let’s explore some common issues and troubleshooting methods related to the material description table in SAP.
Common Issues and Troubleshooting with Material Description Table
While SAP provides a robust system for managing material descriptions, there can be certain issues and challenges that organizations may encounter. Here are some common issues and troubleshooting methods related to the material description table:
- Missing or Incomplete Descriptions: Sometimes, material descriptions may be missing or incomplete, leading to confusion and errors in business processes. To troubleshoot this issue, organizations should review their update processes and ensure that all required fields are populated accurately.
- Inconsistent Descriptions: Inconsistencies in material descriptions can arise when different teams or departments maintain their own set of descriptions. This can cause confusion and errors. To address this issue, organizations should establish clear guidelines for material descriptions and promote collaboration and communication between teams to ensure consistency.
- Data Duplication: Data duplication can occur when multiple entries with similar or identical descriptions exist in the material description table. This can lead to inefficiencies and errors. To resolve this issue, organizations should regularly review and cleanse the material description table, merging or removing duplicate entries.
- Translation Errors: When dealing with multiple languages, translation errors can occur, resulting in inaccurate or misleading descriptions. To mitigate this issue, organizations should implement quality checks and validation processes to ensure accurate translations and consistent language usage.
- Performance Issues: As the material description table grows in size, performance issues may arise when accessing or updating the table. To address this, organizations can optimize the system performance by implementing indexing, archiving, or other performance-enhancing techniques recommended by SAP.
If organizations encounter any issues with the material description table that cannot be resolved internally, it is recommended to seek assistance from SAP support or consult with experienced SAP consultants or experts.
Now that we have explored common issues and troubleshooting methods, let’s discuss enhancements and customizations that can be made to the material description table in SAP.
Enhancements and Customizations for Material Description Table
SAP provides organizations with the flexibility to enhance and customize the material description table to align with their specific requirements. Here are some common enhancements and customizations that can be made:
- Additional Fields: Organizations can add custom fields to the material description table to capture additional information that is specific to their products or processes. For example, in the automotive industry, fields related to engine specifications or vehicle compatibility can be added.
- Field Labels: SAP allows organizations to customize field labels to match their terminology or industry-specific terms. This ensures that the material descriptions align with the organization’s language and understanding.
- Language Support: SAP supports multiple languages, allowing organizations to store material descriptions in different languages. Customizations can be made to add support for additional languages based on the organization’s global operations and customer base.
- Integration with External Systems: Organizations can enhance the material description table by integrating it with external systems, such as product information management (PIM) systems or e-commerce platforms. This integration ensures that material descriptions are consistent across various channels and platforms.
- Workflow and Approval Processes: Customizations can be made to implement workflow and approval processes for updating material descriptions. This helps organizations maintain control and ensure quality checks before new descriptions are published.
It is important to note that any enhancements or customizations made to the material description table should be carefully planned, tested, and documented. It is recommended to involve experienced SAP consultants or experts to ensure that the customizations align with best practices and do not impact system stability.
In conclusion, the material description table in SAP B1 is a critical component for organizations aiming for efficient material management. From its structured framework to customizable features, it stands as a versatile tool for businesses navigating the SAP landscape.