What is ALE in IDoc?
Demystifying ALE in IDoc: A Comprehensive Guide
In the dynamic realm of enterprise application integration (EAI), seamless data exchange across disparate systems is paramount. Within the SAP ecosystem, Application Link Enabling (ALE) and Intermediate Documents (IDocs) form the cornerstone of this communication, ensuring efficient and reliable data transfer. This blog delves into the heart of ALE in IDoc, providing a comprehensive understanding for seasoned SAP users and those embarking on their integration journey.
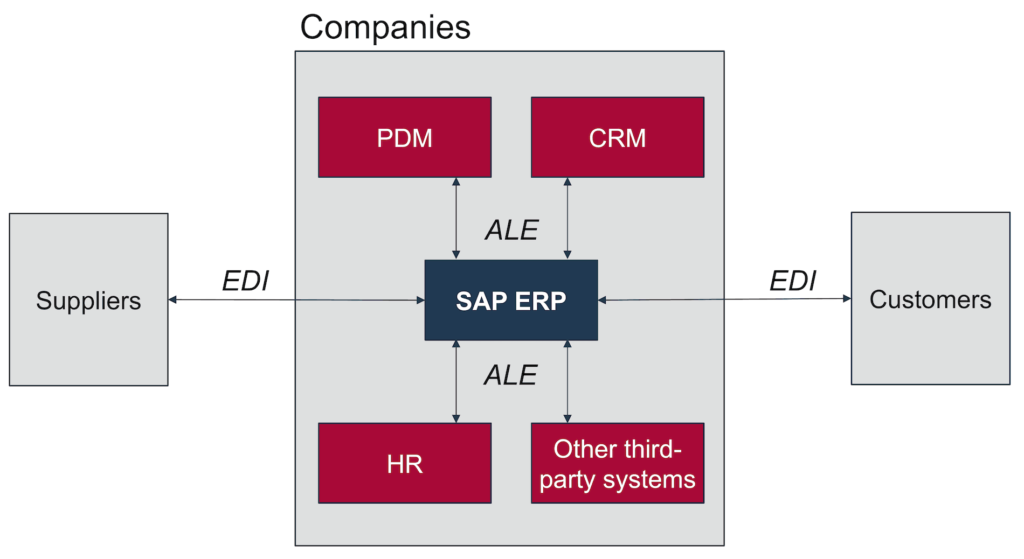
Unveiling the Acronyms: ALE and IDoc Decoded
- Application Link Enabling (ALE): A potent SAP middleware technology orchestrating communication between multiple SAP systems or integrating SAP with external applications. It fosters distributed business processes by decentralizing data, eliminating the need for a central database. ALE functions in both synchronous (immediate response) and asynchronous (delayed response) communication modes.
- Intermediate Documents (IDocs): Standardized data containers acting as the medium for information exchange within ALE. Structured based on pre-defined formats, IDocs bridge the gap between disparate systems, ensuring consistent data interpretation and processing.
Understanding the ALE-IDoc Symphony: Roles and Responsibilities
- IDoc Creation: An application creates an IDoc with relevant data based on a specific message type (e.g., sales order, invoice).
- Outbound Processing: The originating system prepares the IDoc for transmission, converting it to a communication format like Electronic Data Interchange (EDI) if necessary.
- Transmission: IDocs traverse secure communication channels, leveraging RFC (Remote Function Call) for synchronous communication or ALE middleware for asynchronous communication.
- Inbound Processing: Upon reaching the receiving system, the IDoc is parsed, validated, and converted back to its native format.
- Posting: Extracted data from the IDoc is integrated into the target system’s database, updating relevant records or creating new ones.
Key Benefits of Leveraging ALE-IDoc Integration
- Seamless Data Exchange: Facilitates smooth data flow between diverse SAP systems and non-SAP applications, fostering enterprise-wide data consistency.
- Decentralized Architecture: Enables distributed business processes without requiring a central database, enhancing scalability and flexibility.
- Error Handling and Monitoring: Robust error handling mechanisms ensure data integrity and provide visibility into integration processes.
- Security: Secure communication protocols protect sensitive data during transmission, safeguarding business information.
- Scalability and Flexibility: Adapts to varying data volumes and integration needs, supporting agile business evolution.
Common Use Cases for ALE-IDoc in SAP
- Master Data Synchronization: Maintains consistency of customer, product, and other master data across SAP systems.
- Document Exchange: Enables electronic exchange of invoices, purchase orders, and other business documents with trading partners.
- Plant Maintenance Integration: Coordinates maintenance activities and data exchange between plant maintenance systems and SAP.
- Sales and Distribution Integration: Streamlines order processing, delivery, and invoicing by connecting sales and distribution applications to SAP.
- Financial Accounting Integration: Integrates financial data from external systems into SAP’s financial accounting module.
Diving Deeper: Advanced ALE-IDoc Concepts
- Port Types and Message Types: Port types define communication channels, while message types specify the structure and content of data within IDocs.
- Distribution Models: Control how IDocs are routed to specific receivers based on business rules and filtering criteria.
- ALE Interfaces: Custom-developed interfaces tailor ALE integration to specific business requirements.
- ALE Monitoring and Troubleshooting: Diagnostic tools facilitate monitoring IDoc status, identifying errors, and troubleshooting issues.
Best Practices for Successful ALE-IDoc Implementation
- Thorough Planning and Design: Clearly define integration requirements, message types, and error handling strategies.
- Testing and Validation: Conduct rigorous testing to ensure data accuracy, error-free processing, and system compatibility.
- Performance Optimization: Monitor performance metrics and implement optimizations to address bottlenecks.
- Security Considerations: Enforce robust security measures to protect sensitive data during transmission and storage.
- Ongoing Monitoring and Maintenance: Regularly monitor integration processes, address errors promptly, and adapt to evolving requirements.
The Future of ALE-IDoc: Evolution and Integration Advancements
As cloud adoption and integration needs become increasingly complex, ALE-IDoc continues to evolve. Key trends include:
- Cloud-Based Integration: Integration with cloud applications and services, expanding connectivity options.
- API Integration: Leveraging APIs for more flexible and agile integration scenarios.
- Microservices Architecture: Utilizing microservices for granular integration and enhanced scalability.
- Real-Time Integration: Exploring real-time messaging technologies for faster data exchange.
In Conclusion:
ALE and IDoc form the bedrock of data integration within the SAP ecosystem. Their robust capabilities and adaptability have solidified their position as vital tools for businesses seeking seamless communication and streamlined processes. As cloud adoption and integration needs evolve, ALE-IDoc is poised to continue its journey, adapting to new technologies and empowering businesses to thrive in an increasingly interconnected world.
Additional Considerations:
- Industry-Specific Solutions: Explore SAP-provided industry-specific integration solutions to address your vertical’s unique requirements.
- Third-Party Tools and Add-Ons: Consider leveraging third-party tools and add-ons to extend ALE-IDoc functionality and cater to specific needs.
- Community and Support: Actively engage with the SAP community and support resources to stay updated on best practices, troubleshooting tips, and emerging trends.
By incorporating these insights and considerations, you can harness the full potential of ALE-IDoc to achieve efficient and reliable data integration within your SAP landscape, fostering a truly connected and adaptable enterprise.
You may be interested in:
SAP Integration: How to Connect SAP with Other Systems
ALE – Error Handling Through Workflow


