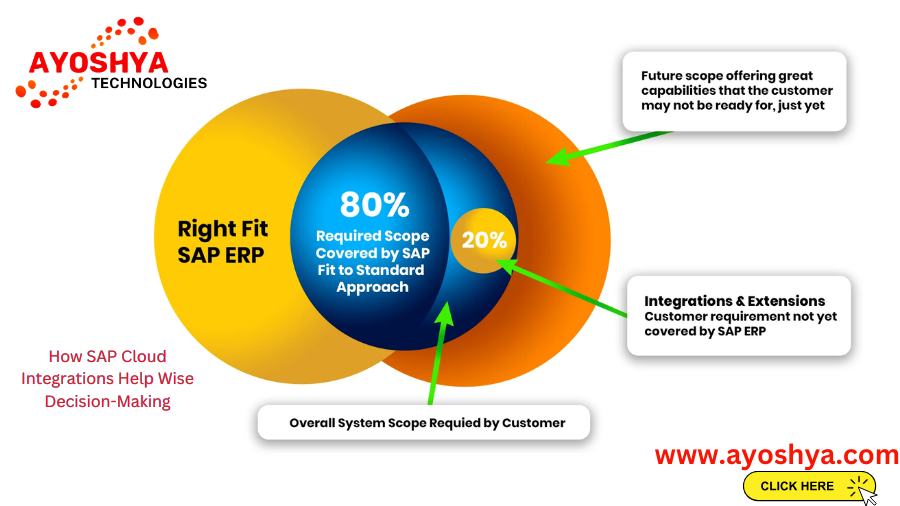
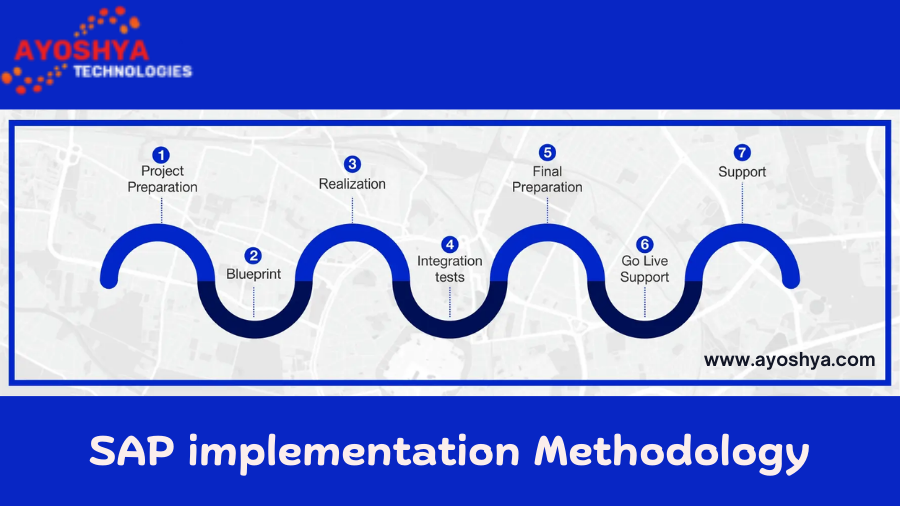
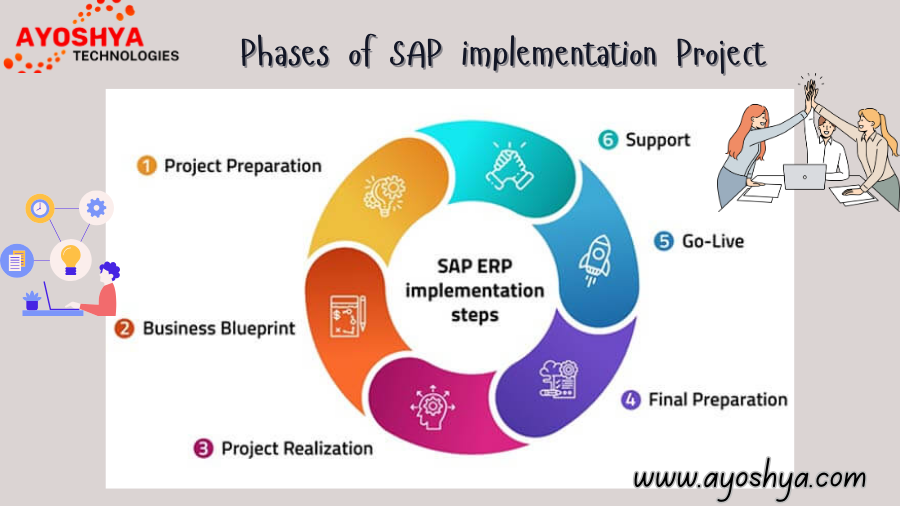
How SAP Cloud Integration Help Wise Decision-Making
Discover how SAP Cloud Integration can enhance your decision-making process by providing real-time data access, improving collaboration, and increasing efficiency. This beginner’s guide explains the benefits and applications of SAP Cloud Integrations for smarter business choices.
A Beginner’s Guide to Leveraging SAP Cloud Integrations for Smarter Business Choices
In today’s rapidly evolving business landscape, making well-informed decisions is critical for maintaining a competitive edge and achieving long-term success. As organizations continue to generate and collect vast amounts of data, traditional decision-making methods often fall short in providing the clarity and speed needed for effective business strategies. Fortunately, SAP Cloud Integrations offer a transformative approach to decision-making by connecting disparate systems, enabling real-time data access, and enhancing overall operational efficiency. This beginner’s guide will delve into how SAP Cloud Integrations can help your business make wiser decisions.
What Are SAP Cloud Integrations?
Understanding the Basics
SAP Cloud Integrations encompass a range of tools and services designed to facilitate seamless connectivity between various cloud-based applications and services. These integrations enable different systems within an organization to communicate and exchange data in real-time, ensuring that information flows smoothly across platforms.
In essence, SAP Cloud Integrations bridge the gap between disparate systems, whether they are on-premises or cloud-based. For instance, a company might use SAP Cloud Integration to connect its Customer Relationship Management (CRM) system with its Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) system. This connection allows data to be synchronized automatically, reducing manual data entry and ensuring consistency across systems.
This integration is not limited to SAP products alone. SAP Cloud Integrations can connect various third-party applications, enabling a more cohesive IT ecosystem. As a result, businesses can achieve greater visibility and control over their operations, facilitating more informed and strategic decision-making.
The Power of Real-Time Data Access
Making Informed Decisions with Up-to-Date Information
One of the most significant advantages of SAP Cloud Integrations is the ability to access real-time data. Traditional decision-making often relies on historical data, which may no longer accurately reflect the current state of the business. In contrast, real-time data provides a current snapshot, allowing decision-makers to respond promptly to emerging trends and issues.
For instance, if your sales team is tracking customer interactions in real-time, they can quickly identify shifts in customer behavior and adjust their strategies accordingly. This agility can be a game-changer in maintaining a competitive edge.
Enhancing Collaboration Across Departments
Breaking Down Silos for Better Decision-Making
In many organizations, different departments work with separate systems that may not communicate with each other. This lack of integration can create data silos, where information is isolated and not easily shared across the organization. SAP Cloud Integrations help break down these silos by enabling seamless data sharing between departments.
Consider a scenario where the marketing department has insights into customer preferences, while the sales team has information on sales performance. By integrating these systems, both teams can access a comprehensive view of customer behavior, leading to more informed and coordinated decision-making.
Improving Efficiency and Reducing Errors
Streamlining Processes for Better Outcomes
Manual data entry and reconciliation are time-consuming tasks that can introduce errors and inefficiencies. SAP Cloud Integrations automate these processes, reducing the need for manual intervention and minimizing the risk of mistakes. By automating data synchronization between systems, organizations can focus on analyzing and acting on the information rather than managing it.
For example, integrating your inventory management system with your e-commerce platform ensures that stock levels are updated in real time. This helps prevent issues such as overselling or stockouts, ultimately improving customer satisfaction and operational efficiency.
Leveraging Advanced Analytics
Turning Data into Actionable Insights
SAP Cloud Integrations not only facilitate data access but also enable advanced analytics. By integrating various data sources, organizations can gain a holistic view of their operations and leverage powerful analytics tools to uncover insights. These insights can then inform strategic decisions and drive business growth.
Imagine having access to comprehensive sales data, customer feedback, and market trends all in one place. With advanced analytics, you can identify patterns, forecast future trends, and make data-driven decisions that align with your business goals.
Scalability and Flexibility
Adapting to Changing Business Needs
As businesses grow and evolve, their needs and processes change. SAP Cloud Integrations offer scalability and flexibility, allowing organizations to adapt their integrations as their requirements shift. This ensures that your integration solutions can grow with your business and continue to support effective decision-making.
For instance, if your company expands into new markets or introduces new products, you can easily integrate additional systems or adjust existing ones to accommodate these changes. This adaptability ensures that your decision-making processes remain effective and relevant.
Conclusion
Harnessing SAP Cloud Integrations for Smarter Decisions
In summary, SAP Cloud Integrations offer a range of benefits that can significantly enhance decision-making within your organization. By providing real-time data access, improving collaboration, increasing efficiency, and enabling advanced analytics, these integrations empower businesses to make informed and timely decisions. As you explore SAP Cloud Integrations, consider how they can be tailored to meet your specific needs and contribute to your overall success.
By embracing these integrations, you can ensure that your business is well-equipped to navigate the complexities of the modern marketplace and make decisions that drive growth and innovation.
you may be interested in this blog here:-
Pre Primary Teacher Training Course Essential Skills
Understanding SAP HANA Cloud Integration