SAP vs. ERP: Choosing the Right Fit for Your Business
Uncertain about sap vs erp? We’ve got you covered! Explore the key differences, functionalities, and ideal use cases. Discover which solution empowers your business growth…
Feeling overwhelmed by the maze of acronyms in the business world?** Struggling to decipher the difference between sap vs erp and how they can impact your organization? You’re not alone! Many businesses grapple with this very confusion, unsure of whether SAP is synonymous with ERP or if there’s a hidden world of options beyond this industry giant. But fear not, weary entrepreneur! This comprehensive guide will demystify the maze, shedding light on the key distinctions between SAP and ERP. We’ll explore their functionalities, ideal use cases, and empower you to choose the right fit to ** propel your business growth**. So, buckle up and get ready to unveil the secrets behind these powerful acronyms!
Understanding ERP: The Backbone of Integrated Business Management
Imagine a central hub where all your crucial business operations, from finance and accounting to inventory management and customer relationships, seamlessly interact and share information. This is the essence of Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP), a powerful software solution designed to streamline operations, improve efficiency, and empower data-driven decision-making.
Core Functionalities of ERP Systems:
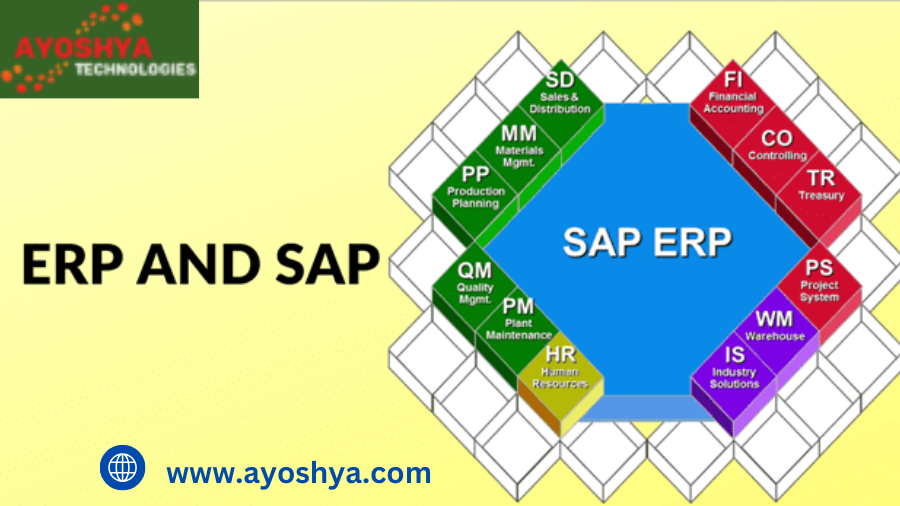
- Financial Management: ERP systems consolidate and automate various financial tasks, including accounts payable and receivable, general ledger, budgeting, and financial reporting. This ensures real-time financial visibility and facilitates informed financial decision-making.
- Supply Chain Management: From procurement and inventory control to production planning and logistics, ERP systems orchestrate the flow of goods and materials throughout your supply chain. This enables optimized inventory levels, reduced costs, and improved delivery times.
- Customer Relationship Management (CRM): ERP systems integrate customer data and interactions, fostering improved customer service, targeted marketing campaigns, and enhanced sales opportunities.
- Human Capital Management (HCM): Some ERP systems also encompass functionalities like payroll processing, talent management, and employee self-service, streamlining human resource processes and improving employee engagement.
Beyond the Core: Industry-Specific Solutions:
While the core functionalities mentioned above form the foundation of most ERP systems, many vendors offer industry-specific solutions tailored to address the unique needs of different sectors. These solutions often include pre-configured workflows, industry-specific reporting tools, and integrations with specialized industry applications. For example, an ERP solution for a manufacturing company might include functionalities for production planning, quality control, and shop floor management, while a solution for a healthcare organization might focus on patient record management, billing, and claims processing.
Unveiling SAP: The Powerhouse Player in the ERP Landscape
While ERP represents a broader category of software solutions, SAP stands out as a prominent vendor within this domain. SAP offers a comprehensive suite of ERP products catering to various business sizes and industry needs. However, it’s crucial to understand that SAP is not synonymous with ERP. Let’s delve deeper into the unique characteristics of SAP solutions:
Depth and Industry-Specific Focus:
Unlike generic ERP systems that offer a broader range of functionalities across various departments, SAP solutions often go deeper in specific areas. They provide industry-specific features and functionalities tailored to address the unique challenges and requirements of different sectors. For example, SAP offers specialized solutions for manufacturing, healthcare, retail, and many other industries. These solutions leverage industry best practices and deep domain expertise to optimize processes, improve efficiency, and deliver tangible business value within specific contexts.
A Spectrum of Products for Diverse Needs:
Recognizing that businesses come in all shapes and sizes, SAP offers a spectrum of ERP products catering to different levels of complexity and budget constraints. Some popular examples include:
- SAP S/4HANA: A next-generation ERP suite built on the SAP HANA in-memory database platform, offering real-time insights, improved performance, and advanced analytics capabilities for large enterprises.
- SAP Business One: A cloud-based ERP solution designed for small and mid-sized businesses, providing core functionalities like financials, CRM, and inventory management in a user-friendly interface.
- SAP Business ByDesign: Another cloud-based ERP solution targeted towards mid-sized businesses, offering pre-configured industry-specific processes and functionalities.
Key Differences Between SAP and ERP: Choosing the Right Fit
Now that we’ve explored both ERP and SAP in detail, it’s time to shed light on the crucial distinctions between these two entities. Understanding these differences is paramount for making informed decisions when selecting the most suitable solution for your organization’s needs. sap vs erp
1. Vendor vs. Category:
- ERP: Stands for Enterprise Resource Planning and represents a broad category of software solutions offered by various vendors like SAP, Oracle, Microsoft, and others. These solutions aim to integrate and automate various core business functions across departments.
- SAP: Represents a specific software vendor within the ERP landscape. SAP offers a comprehensive suite of ERP products catering to diverse business needs, but it’s not the only player in the market.
2. Functionalities:
- ERP: Generally offers a broader range of functionalities across various departments, including finance, accounting, supply chain, CRM, HCM, and more. However, the depth and specific features may vary depending on the vendor and chosen product.
- SAP: Often provides deeper functionalities in specific areas, particularly within industry-specific solutions. These solutions cater to the unique needs of different sectors and may offer more advanced features and functionalities compared to generic ERP offerings in those areas.
3. Scalability and Customization:
- ERP: Offers varying degrees of scalability and customization depending on the chosen vendor and product. Some generic ERP systems may be highly customizable to fit specific business needs, while others may offer limited customization options.
- SAP: While SAP products offer a certain level of customization, they generally require more expertise and resources to implement and adapt to specific needs compared to some generic ERP systems. However, SAP’s industry-specific solutions often come pre-configured with industry best practices, reducing the need for extensive customization.
4. Cost and Implementation:
- ERP: The cost of ERP systems can vary significantly depending on the vendor, chosen product, and required customizations. Implementation complexity can also vary, with some generic ERP systems offering easier and faster deployment compared to others.
- SAP: SAP solutions are generally considered more expensive than some generic ERP options, particularly for larger and more complex implementations. Additionally, due to the depth and industry-specific nature of SAP solutions, implementation can involve greater complexity and require specialized expertise.
Unveiling the Mysteries of SAP vs. ERP
Your exploration into the world of sap vs erp has opened doors to valuable insights. But you might still have lingering questions. To ensure you have all the information necessary to make informed decisions, let’s delve into some frequently asked inquiries:
1. What are the benefits of using an ERP system?
Implementing an ERP system can bring a multitude of advantages to your organization, including:
- Improved efficiency and productivity: Streamlined processes, automated tasks, and real-time data visibility empower your team to work smarter and faster.
- Enhanced data accuracy and consistency: Eliminating data silos and manual entry ensures consistent and reliable information across all departments.
- Better decision-making: Data-driven insights from integrated information empower informed choices for strategic growth and improved performance.
- Increased collaboration and communication: A unified platform fosters seamless communication and collaboration between departments, breaking down information barriers.
- Reduced costs: Optimized inventory management, improved resource allocation, and streamlined processes can lead to significant cost savings.
2. What are some popular alternatives to SAP?
While SAP is a prominent player, the ERP landscape offers various alternatives to consider:
- Oracle NetSuite: A cloud-based ERP solution known for its scalability and flexibility, catering to a wide range of industries.
- Microsoft Dynamics 365: A suite of cloud-based business applications, including ERP functionalities, offering integration with other Microsoft products.
- Infor CloudSuite: A comprehensive cloud-based ERP suite with industry-specific solutions and strong financial management capabilities.
- Epicor ERP: A popular choice for manufacturing companies, offering robust production planning, inventory management, and shop floor control functionalities.
The best alternative for your organization depends on factors like your industry, budget, specific needs, and existing technology infrastructure.
3. Is SAP too complex for small businesses?
While SAP offers powerful solutions, its complexity and cost can be daunting for smaller businesses. However, SAP Business One addresses this concern by providing a user-friendly, cloud-based ERP solution specifically designed for the needs of small and mid-sized businesses. It offers core functionalities like financials, CRM, and inventory management in a scalable and cost-effective package.
4. What are the implementation challenges associated with ERP systems?
Implementing an ERP system requires careful planning and consideration of potential challenges:
- Data migration: Transferring existing data to the new system accurately and efficiently can be complex and time-consuming.
- Change management: Encouraging user adoption and adapting to new processes can require effective communication, training, and support.
- Integration with existing systems: Ensuring seamless integration with existing software applications can involve technical complexities.
- Cost and budget management: Implementing and maintaining an ERP system requires careful budgeting and resource allocation.
Conclusion
Charting Your Course Towards Optimal Business Operations
The journey through the maze of SAP vs. ERP has hopefully shed light on the distinctions, functionalities, and ideal use cases of each. You’ve explored the core functionalities of ERP systems, encompassing everything from financial management to customer relationship management. You’ve unveiled the depth and industry-specific focus of SAP solutions, catering to diverse business needs. Most importantly, you’ve gained insights into the key differences between these two entities, empowering you to make informed decisions for your organization.
Remember, the ideal solution hinges on your specific business size, industry, budget, and unique requirements. Carefully consider the benefits of ERP systems, including improved efficiency, enhanced data accuracy, and better decision-making. Explore the spectrum of options available, including SAP solutions and popular alternatives. If embarking on an ERP implementation, acknowledge the potential challenges and develop a strategic plan to ensure success.
As you navigate this crucial decision, remember that investing in the right solution can be a game-changer for your business. Embrace the power of integrated data, streamlined processes, and data-driven insights to propel your organization towards sustainable growth and long-term success. Don’t hesitate to seek guidance from experienced professionals to gain tailored recommendations and ensure a smooth implementation journey. With the knowledge gleaned from this exploration and a proactive approach, you can confidently chart your course towards optimal business operations in the ever-evolving technological landscape.
you may be interested in this blog
Adding Process Controls & Approval Form
Bridging the Gap Guide to FI-SD Integration in SAP