Understanding Transactional Data
In the realm of data processing, understanding transactional data is paramount for businesses seeking operational efficiency and strategic decision-making. Today, we delve into the intricacies of transactional data, unraveling its significance and practical applications.
What is Transactional Data?
Transactional data, with regards to information the board, is the data recorded from exchanges.
An exchange, in this unique situation, is a grouping of data trade and related work, (for example, data set refreshing) that is treated as a unit for the reasons for fulfilling a solicitation. Transactional data can be monetary, calculated or business related, including everything from a buy request to delivery status to worker hours worked to protection expenses and claims.
As a piece of value-based records, conditional information is gathered with related ace information and reference information. Transactional data records a period and pertinent reference information required for a specific exchange record.
Importance of Transactional Data in Business
1. Real-time Insights
Transactional data provides real-time insights into the day-to-day operations of a business. By analyzing these data points, organizations can make informed decisions promptly, fostering agility in response to market changes.
2. Decision-Making Precision
In strategic decision-making, precision is key. Transactional data offers a granular view, allowing businesses to identify trends, patterns, and anomalies, enabling more accurate decision-making.
3. Operational Efficiency
Efficient business operations rely on a thorough understanding of transactional data. From inventory management to customer interactions, every operational facet benefits from a comprehensive grasp of transactional details.
Bonus: An Overview of SAP Material Management
Analyzing Transactional Data
1. Data Structure
Transactional data is often structured in a tabular format, with each row representing a specific transaction and columns detailing relevant attributes. The structure may vary based on the type of transaction and industry standards.
2. Granularity
The granularity of transactional data determines the level of detail captured. High granularity provides intricate details of each transaction, while lower granularity aggregates data for broader insights.
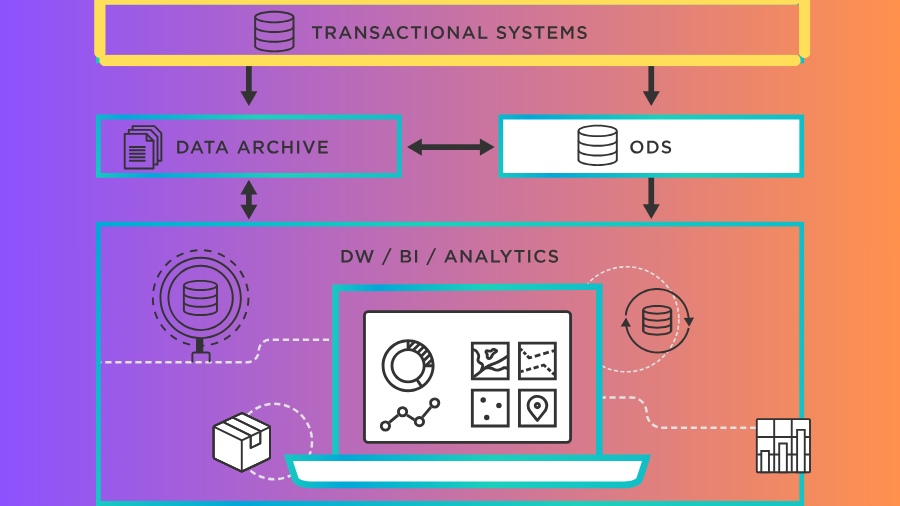
3. Integration with Business Intelligence
Integrating transactional data with robust business intelligence tools enhances analytical capabilities. Visualization tools and dashboards can transform raw data into actionable insights.
Instances of Transactional Data
Transactional Data regularly falls under the classification of organized information. A few models include:
- Monetary Transactional Data: protection expenses and claims information, or a buy or deal; Stores or withdrawals if there should be an occurrence of banks
- Calculated conditional information: delivering status, transporting accomplice information
- Business related Transactional Data: representative hours following
In this specific situation, conditional information records the reference information, including time, to report a specific exchange. It is recorded as a feature of the data and applications frameworks that computerize the key business cycles of an association, for example, online exchange handling frameworks.
What do you mean by transactional RFC?
Contingent upon the idea of the exchange, the information gets gathered inside ace information with related item data and charging data.
Crude Transactional Data can be chaotic and should be cleaned for downstream investigation. Information enhancement devices are currently generally accessible for this reason.
Best Practices for Managing Transactional Data
1. Robust Database Management
Ensuring a robust and scalable database management system is essential for handling large volumes of transactional data. This includes optimizing data storage, retrieval, and processing capabilities.
2. Data Security Measures
Given the sensitive nature of transactional data, implementing stringent security measures is imperative. This includes encryption, access controls, and regular audits to safeguard against unauthorized access.
3. Regular Data Maintenance
Transactional data can accumulate rapidly. Regular data maintenance, including archiving and purging obsolete records, is crucial for system performance and data accuracy.
Who Utilizations Conditional Information in an Association?
In an association, the data innovation functional group and the information examination group are the principal overseers of Transactional Data. The advantages are two-crease:
1. Data innovation tasks screen exchanges progressively. They utilize the information and streaming items to find, analyze, and fix any exhibition gives that might cause serious help disturbances. This sets aside both cash and time.
2. Business directors and information examiners utilize continuous exchange information to grasp purchaser conduct and find out about how their items and administrations are embraced. In this occurrence, the exchange information yields significant bits of knowledge that assist with further developing the help offering. Exchange information conveys better client encounters, gain new business, and lift productivity of the business.
Ace and transactional data
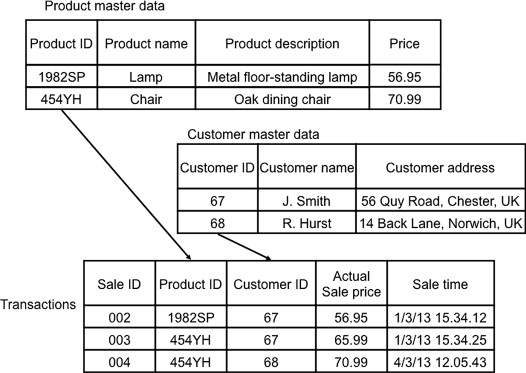
Transactional data connects with the exchanges of the association and incorporates information that is caught, for instance, when an item is sold or bought. Ace information is alluded to in various exchanges, and models are client, item, or provider information. By and large, ace information doesn’t change and needn’t bother with to be made with each exchange. For instance, on the off chance that one client buys numerous items at various times, an exchange record should be made for every deal, except the information about the client remains something similar. Figure 12.1 shows how ace information frames part of a conditional record. For this situation, when the light and seat items are sold, the exchange references the pertinent item IDs and client IDs. The item and client records, assuming they as of now exist, needn’t bother with to be reproduced or adjusted for this new exchange. Different information in the exchange, like the remarkable identifier for the exchange (i.e., deal ID) and deal time do, nonetheless, need to change. Exchange information is hence normally more unstable than ace information as it is made and changes all the more much of the time. Note that this straightforward model shows the real deal cost in the exchange and cost of the item in the expert information. There are various ways of demonstrating this, yet the model demonstrates the way that the genuine cost can change contingent upon the exchange and it might just be determined from the item cost in the expert information (in the wake of including limits, and so on.). Exchange 003 in Figure 12.1 shows that a markdown has been applied to the retail cost.
Sign in to download standard size picture
FIGURE 12.1. Ace and transactional data.
One more property of expert information is that it is many times shared and utilized by various specialty units. For instance, a client record will be utilized by promoting as well as deals. Issues emerge when one specialty unit refreshes the expert record and doesn’t illuminate the other specialty unit. For instance, the promoting division could refresh the location of a client and, on the off chance that they don’t illuminate the outreach group, requests could be shipped off an obsolete location.
Albeit these are the overall properties of expert and data, there are events when these information types act contrastingly and, subsequently, this differentiation becomes obscured. For instance, ace information can likewise have all the earmarks of being conditional when changes to a provider address, for example, are not overwritten in a record, however rather another record is made. An association might decide to hold all past locations of a provider, particularly on the off chance that they wish to investigate a provider’s development. It merits focusing on cases, for example, these, in light of the fact that it very well might be smarter to apply conditional answers for the issues in this information type so it is overseen accurately.
Action TIP
Try not to constantly accept that ace information should be treated with just expert information related arrangements, particularly assuming the expert information acts like conditional information.
Conclusion
In conclusion, a nuanced understanding of transactional data is pivotal for businesses navigating the complexities of modern commerce. From real-time insights to informed decision-making, the impact of data is far-reaching. By implementing best practices and leveraging advanced analytics, businesses can not only manage but thrive on the wealth of transactional information at their disposal.
FAQs related to Transactional Data
1. What is an example of a data transaction?
It is a structured data category that describes an internal or external event or transaction that takes place as an organization conducts its business. Examples include:
Purchases, Returns, Invoices, Payments, Credits, Debits, Trades, Dividends, Sales orders, Shipping documents, Credit card payments, Insurance claims.
2. What is the difference between transactional data and operational data?
It captures the progress of specific business transactions, focusing on details such as item purchases, order modifications, status changes, purchases, payments, transfers, transaction dates, amounts, and instruments used to complete sales. On the other hand, operational data encompasses a broader scope, including all other data that supports day-to-day operations. This includes monitoring and managing ongoing transactions within the system, making decisions about resource allocation, and actively working towards improving overall business processes.
3. What is the difference between transactional data and non transactional data?
A non-transactional data set doesn’t ordinarily uphold transactions similarly as a transactional database. Many NoSQL databases are for the most part intended for high adaptability and adaptability, and may forfeit some value-based assurances to accomplish these objectives.
4. What is a transaction in data mining?
It will be data that is caught from transactions. It records the hour of the exchange, where it happened, the costs of the things purchased, the installment strategy utilized, limits if any, and different amounts and characteristics related with the exchange.