sap implementation process
SAP Implementation Process | Phases of ASAP Methodology
SAP ERP smoothes out the majority of the cutting edge business processes, yet a legitimate sap implementation process is significant for the successful work process of the association. Besides, cautious contemplations and key arranging are expected for augmented results post the execution of SAP ERP.
Quickly technique is a basic piece of the product advancement life cycle for SAP execution projects. The quickly philosophy partitions the SAP execution project into significant stages or achievements that should be accomplished for fruitful SAP execution.
What is ASAP methodology in SAP?
ASAP methodology is basically the strategy by which the framework programming of SAP is executed over the business server, consequently working with work productivity and business activities. The appropriate execution of the ASAP apmethodology proach guarantees work process the executives and assessment as well as deals with the related gamble.
What are the steps of the SAP implementation process?
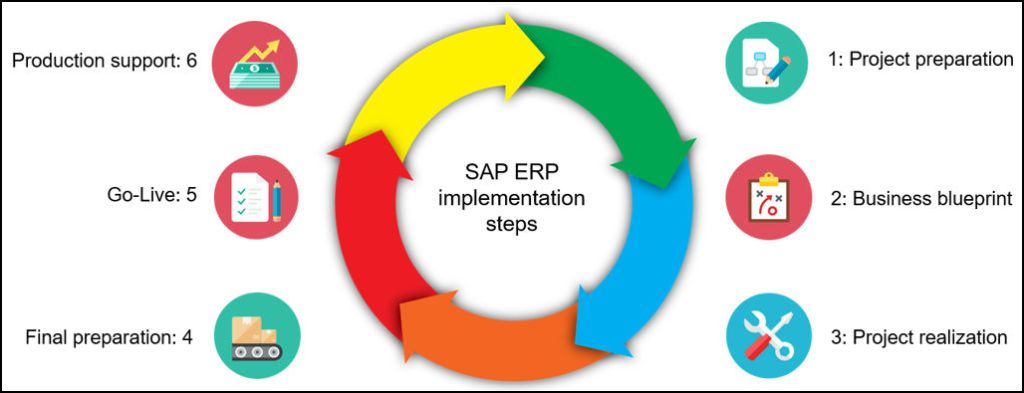
The quickly philosophy proposes sequential strides for fruitful SAP execution. A point by point outline of these means has been given beneath,
Project Preparation
The most important phase in the SAP execution process is project readiness that is, setting up an effective guide, according to the business prerequisites and functionalities.
In this step of the SAP execution process, arranging capabilities are performed, following the different factors and subtleties of the business prerequisites. This stage sets the standard for fruitful SAP execution and requires vital dynamic on specific variables, for example,
- Defining project goals and objectives
- Establishing the scope of implementation
- Arranging the task arrangement, financial arrangement, and execution plan
- Setting up the venture association and assigning assets
Business Diagram
Following the undertaking planning, the assets are designated based on the standards and prerequisites for the new framework. The mix details, connection point, and interaction maps are laid out from now on.
This step of the SAP execution process includes the presentation of hole investigation which suggests the review and examination of contrasts between two data frameworks or applications to decide the most common way of relocating to the new state.
When the distinctions have been distinguished, considered, and assessed, a business plan is set down. This business outline incorporates the expected business information lined up with the different business objectives and the further targets to be laid out. Consequently, a structure is organized as per the different goals of the business and the ongoing information investigation.
Acknowledgment
When the business outlines have been laid out, standard design is played out, that is to say, arranging the SAP execution rules based on the outcomes got from plans and the business objectives.
The utilitarian specialists complete the arrangement steps in this stage and the handling is finished in this step of the SAP execution process. Followed by arrangement, different testing systems are completed for the smooth working of the business.
Last Readiness
When the acknowledgment has been effectively completed, last arrangements are finished in the SAP execution process. This incorporates testing, preparing, framework the executives, and last cutovers to determine any necessary issues to be settled. Consequently, it is essential to guarantee that every one of the prerequisites of the business are being satisfied in this phase of SAP execution.
Ace information is transferred to the new framework utilizing LSMW, BADI, and BAPI. Then, at that point, the client begins utilizing the SAP framework. End-client preparing is given to individuals working at the client’s end. To put it plainly, the venture goes live.
Different testing strategies are gone through in this stage, for example, responsibility testing, reconciliation testing, and fictitious testing. It is vital to perform support checks in this phase of the SAP execution process for ideal execution.
Go-Live and Support
The last move toward the SAP execution process is going live with the new framework and utilizing this recently carried out SAP framework for the business processes.
In addition, it is likewise guaranteed that the framework is moving along as expected. Here, different help and emotionally supportive networks are given to fix any harms and work with a smooth work process.
How to track down the best Drain MSP?
- The decision of a SAP oversaw specialist co-op guarantees the smooth organization, the board, and observing of the SAP ERP arrangement. Examined beneath are the imperatives of a decent SAP MSP for smooth business working,
- Specialized Abilities: The right SAP MSP should have satisfactory involvement with SAP execution and handling. They should be furnished with the right specialized abilities and can propose the right approaches, structures, and practices for executing and dealing with the SAP ERP framework.
- Decreased costs: The ideal SAP MSP will help with bringing down the expense of tasks so the labor force can zero in on the center business activities. With the right SAP MSP, you get the right arrangement of mastery and administrations to accomplish your business activities, at the right expense.
- Improved security: With the right SAP MSP, you move a solid climate to get rid of all the potential digital dangers and security difficulties and appreciate total consistence the board.
You may be interested in:
SAP CPQ – Business Process flow for Back-end Integrations
Future of ERP : The Next Big thing in ERP