What is SAP Datasphere ?
What is SAP Datasphere
SAP Datasphere, the up and coming age of SAP Information Distribution center Cloud, is an exhaustive information administration that empowers each datum expert to convey consistent and versatile admittance to crucial business information.
It was inevitable until SAP’s SaaS Cloud system prompted the presentation of an undertaking information distribution center (EDW) arrangement: SAP Datasphere (already SAP Information Stockroom Cloud).
SAP Datasphere functions admirably with SaaS kinds of source frameworks as you can have the establishment in a similar specialized climate. This considers the most ideal transmission of information from the source to the EDW and consequently enjoys a benefit in the transfer from a cloud-based answer for a nearby distribution center.
Software Development At SAP: Microservices
What is in a general sense different with SAP Datasphere is the way that it doesn’t follow the standard of the ideal kind of information stockroom fair and square. Interestingly, it follows the standards of the requirements of the buyers, and it begins little and basic (however this doesn’t imply that an intricate information distribution center arrangement can’t be laid out). Intricacy can without much of a stretch lead to a gamble of huge execution suggestions that the end client can’t see. With this, the actual arrangement can be considered having two primary subjects:
- The semantic layer is for simple, self-administration type treatment of information sources, associations, and changes. The information stockroom layer is the underpinning, everything being equal, to be gathered and blended. This last option layer, which SAP call the information layer concerns building perspectives to act as essential hotspot for the semantic layer.
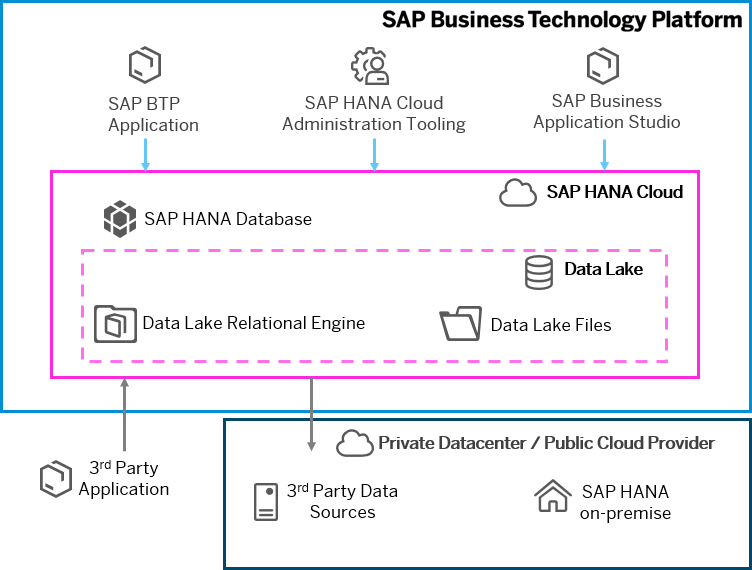
- The engineering of the actual arrangement shows that the methodology is, like SAP BW/4HANA, an application kind of arrangement. Yet, the likelihood to use SQL abilities makes it especially fascinating for those organizations that have been involving SQL-based answers for their EDWs. The figure underneath shows every one of the parts of the arrangement and the arrangements it can incorporate with.
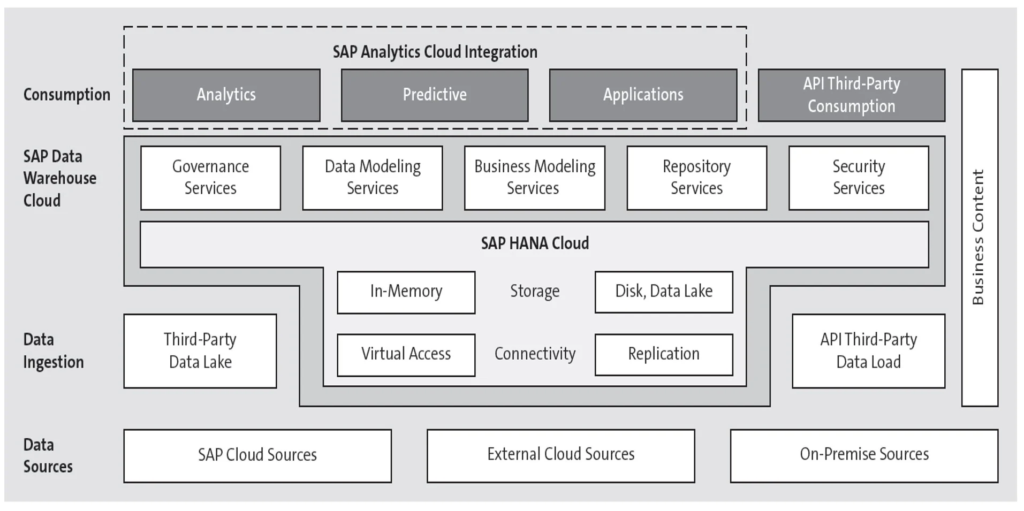
The convenience benefits can be found in straightforward graphical displaying of information structures; the simplicity of adding informational collections on nearby drives or any information source, be they information lakes or basic level documents in the replication choices of the semantic layer, is upheld by prebuilt connectors. SAP discusses a business developer, which mirrors this approach quite well. Coincidentally, when we discuss information lakes, we additionally incorporate SAP HANA information lakes, which can be empowered through Open SQL compositions.
The openness of these capabilities straightforwardly from inside the connection point of a SAP Examination Cloud arrangement underlines the idea of focusing on shoppers in business divisions. It upholds a hierarchical way to deal with make an information distribution center, taking into consideration a hierarchical layer with a subset of the demonstrated items and in this manner considering endeavor wide joint effort, utilizing the purported space idea. As it were, there is a similarity with Universes. Albeit the business content for this arrangement isn’t really that rich for SAP BW/4HANA, it exists and will be improved after some time.
One exceptional resource of the new improvement is the way to deal with and acknowledgment of a full mix with basic information models of SAP BW/4HANA or SAP S/4HANA. The circumstance presently in SAP Datasphere is a quantum jump ahead in the adaptable association with SAP-began frameworks and the evasion of twofold support of information models (reproducing space models). An intriguing reality is the reuse of SAP Information Knowledge abilities for the information transfer capacities.
Certainly, there is still a ton to be worked to finish the methodology and to conquer execution holes because of missing usefulness, however the ideas and the ventures are genuine and the tasks are running. These are motivations to be energized!
For those organizations or associations that have picked a SaaS kind of ERP framework with SAP S/4HANA Cloud, fundamentals release, all things considered, the SaaS-based SAP Datasphere is the primary EDW to consider. The information is in a similar climate, the cloud procedure is upheld, and most of purpose cases are either not perplexing or principally little in nature. So why not start with this end-client arranged approach?
By and large, while organizations running SAP S/4HANA are new to information warehousing or are involving an ERP framework from SAP interestingly, it’s smart to likewise suggest investigating SAP Datasphere. The hierarchical way to deal with vanquishing the information stockroom task is a main justification for this proposal.
What are the functionalities of SAP Datasphere?
1. Space management :
A virtual work area in SAP Datasphere is a store of information addressing a particular business portion. The arrangement of work areas makes it conceivable to give unified and secure demonstrating conditions for various divisions or use cases. Executives can make work areas, designate extra room (plate and memory), characterize their need, add clients and relegate jobs to them, and use checking and logging devices.
2. Data integration :
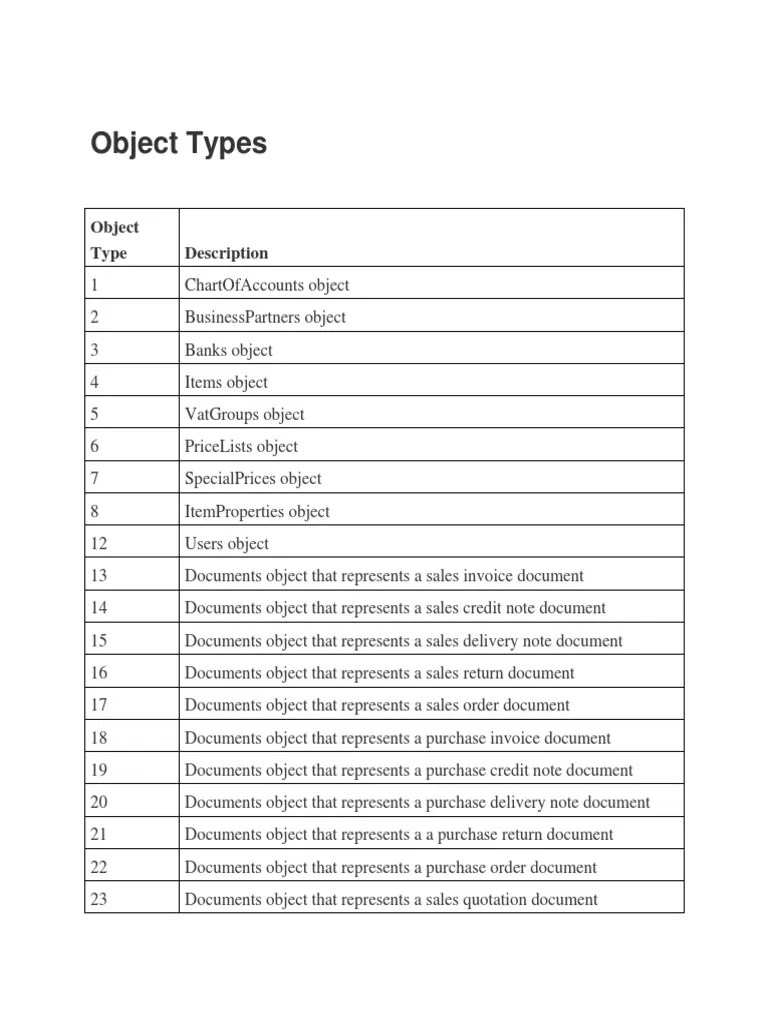
SAP Datasphere empowers clients to import information from many sources (cloud, on-premise, SAP information, non-SAP information). The following is a rundown of the association types accessible in SAP Datasphere :

3. Data modelling in Data Builder :
Data Builder is a displaying supervisor with a worked on interface. It permits you to join, clean and plan information for use in information compensation devices like SAP Examination Cloud or for demonstrating in Information Developer. It offers the choice of bringing in information from CSV or CSN/JSON documents.
It offers clients various elements to assist them with dealing with their information all the more successfully :
- Making graphical perspectives: empowers you to make a view from at least one information sources.
- Table creation: permits you to make tables containing information by characterizing their designs.
- Making relationship models: used to import, alter, view and convey information substances (tables, sees, and so on.)
- Make SQL sees: Permits you to make sees from a SQL proofreader that can be utilized to question sources.
- Making logical models: empowers you to make a scientific model as a reason for utilization in SAP Examination Cloud.
- Making of information streams: empowers information to be removed, changed and stacked from a natural connection point.
- Production of replication streams: empowers information to be duplicated from objects in a similar source (Compact discs sees, tables, ODP object) to a similar objective.
- Make keen pursuits: Empowers information from two elements to be blended regardless of whether there is an issue with the join.
- Making of errand affixes : permits you to gather a few substances
4.Data modelling in Business Builder:
Business Manufacturer allows you to join, refine and enhance protests previously made in Information Developer. It can likewise be utilized to make specialty units, utilization models and viewpoints for use in SAC.
Business Builder permits you to :
- Make new aspects: Permits you to make examination tomahawks.
- Make new reality tables: Permits you to make truth tables with estimations.
- Make a reality model : This permits you to make a model that gathers business substances of current realities and aspects type.
- Import SAP BW/4HANA models: permits you to import insightful questions from SAP BW/4HANA.
- Formation of an authorisation situation: used to control admittance to existing information. Every client approaches the significant information as indicated by their job.
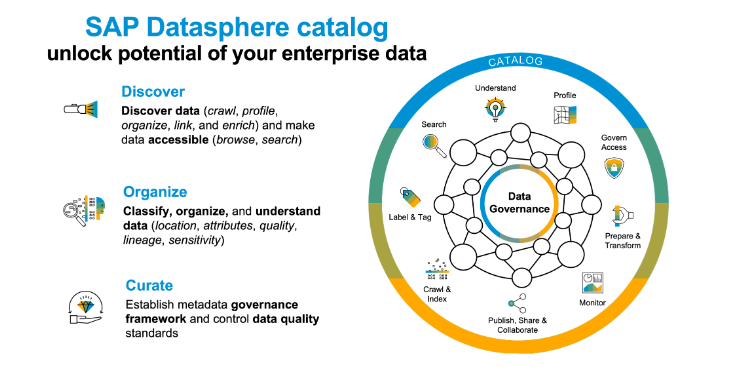
5. SAP Datasphere Catalog :
The SAP Datasphere index is a thorough arrangement that gathers and coordinates metadata. It empowers :
- Deal with all framework objects by giving a worked visible of information scenes.
- Access solid information for quality demonstrating.
- Information genealogy and effect examination
- Metadata administration
Conclusion
SAP Datasphere marks a significant evolution in SAP’s data management solutions, offering a consumer-centric approach to enterprise data warehousing. Its flexibility, seamless integration with SAP systems, and emphasis on user-friendly features make it a compelling choice for organizations, particularly those utilizing SaaS-based ERP systems like SAP S/4HANA Cloud. The platform’s functionalities, including robust domain management, versatile data integration, and powerful data modeling tools, contribute to its appeal in the ever-evolving landscape of data management.
FAQs:
- What sets SAP Datasphere apart from traditional data warehouses?
- SAP Datasphere distinguishes itself by prioritizing consumer needs over rigid data warehouse standards. It starts small and simple, emphasizing user-friendly features and flexibility while still accommodating complex data warehouse solutions.
- How does SAP Datasphere support organizational collaboration?
- The platform facilitates a hierarchical approach to data warehouse creation, allowing for an organizational layer with subsets of proven products. This enables enterprise-wide collaboration using a domain concept, similar to Universes in SAP BW/4HANA.
- Why is SAP Datasphere recommended for organizations using SAP S/4HANA Cloud?
- For organizations leveraging SAP S/4HANA Cloud, SAP Datasphere becomes a prime choice as it operates in the same environment, aligns with the cloud strategy, and addresses most use cases efficiently, especially those that are not overly complex.
- What are the key functionalities of SAP Datasphere’s Data Builder?
- Data Builder offers a user-friendly interface for data modeling, allowing users to create graphical views, tables, relationship models, SQL views, logical models, data flows, replication streams, smart searches, and task chains for effective data management.
- How does SAP Datasphere Catalog contribute to data management?
- The SAP Datasphere Catalog is a comprehensive solution for metadata management, offering a visual representation of data landscapes, ensuring data quality modeling, providing data lineage and impact analysis, and facilitating metadata management for enhanced control and understanding of the data environment.
Read More Blogs:
Power of Oracle ETL: A Comprehensive Guide
SAP brings S/4 HANA Cloud and SAP Commerce Cloud on India data