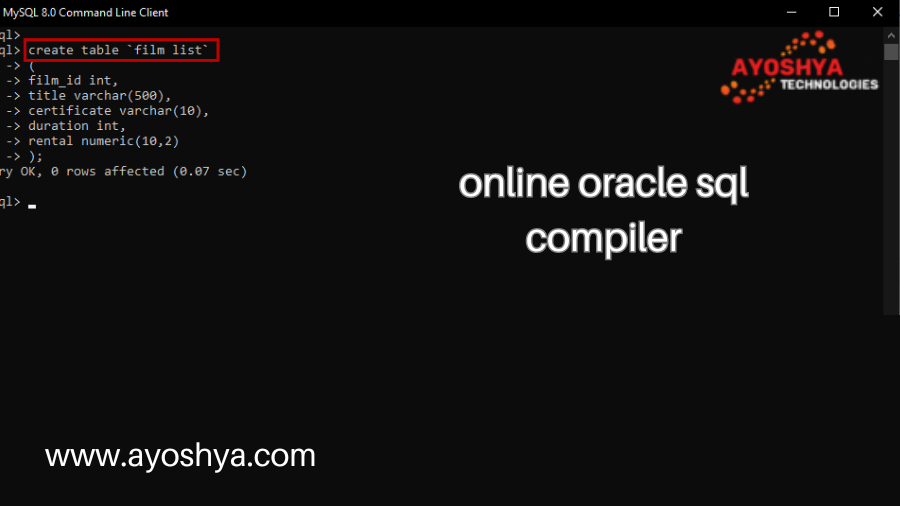
Top Online Oracle SQL Compiler for Effortless Development
online oracle sql compiler, Ditch the installation hassle! Explore the best online Oracle SQL compilers to write, test, and debug your queries… instantly.
From Project Chaos to Control: Mastering WBS Elements in SAP
Do you ever feel like your projects are a swirling vortex of tasks, deadlines, and dependencies? You’re not alone. Complex projects can quickly spiral out of control, leaving you feeling overwhelmed and unsure where to begin. But fear not, project warriors! There’s a powerful tool within SAP’s Project Systems (PS) module that can transform your project from chaotic mess to a meticulously planned masterpiece: Work Breakdown Structures (WBS) elements.
WBS elements are the building blocks of effective project management in SAP. They act as a hierarchical structure, meticulously breaking down your project into manageable chunks. This allows you to visualize the project scope, identify dependencies, and assign resources efficiently. Essentially, WBS elements become your roadmap to project success, guiding you every step of the way.
Creating WBS Elements in SAP
Before diving into the creation process, it’s crucial to understand the functionalities within SAP that will empower you. Here’s what you’ll need:
- Access to the SAP PS Module: The Project Systems (PS) module is the heart of project management in SAP. It provides the tools and functionalities specifically designed to handle project lifecycles, including creating and managing WBS elements. If you’re unsure about your access, consult your system administrator.
- Authorization for WBS Creation: Within the PS module, specific authorizations are required to create WBS elements. These authorizations control who can create, edit, and delete WBS elements within a project.
Now, let’s get started with the creation process! We’ll utilize the transaction code CJ20N, which stands for “Create Project and WBS Element.”
2.1 Project Definition & WBS Element Creation
- Launch CJ20N. The Project Builder screen appears.
- Click the “Create Project” button (second dropdown menu on the top left corner). A pop-up window titled “Define Project” will appear.
Here’s where you define the overall project and create your first WBS element:
- Project Definition: Enter the Project ID according to your company’s naming conventions. This unique identifier will be used throughout SAP to reference the project. You’ll also define essential details like the project description, planned start and finish dates, and a person responsible for the project.
- WBS Element Creation: By default, SAP creates the first WBS element automatically with the ID “001“. This element represents the entire project itself. You can modify the description of this element to better reflect the overall project scope.
2.2 Entering Basic Data for the WBS Element
Once you’ve defined the project and created the initial WBS element, the system displays the detailed screen for WBS element 001. Here, you can specify various attributes that define the element’s characteristics:
- Short Text & Description: Provide a concise yet informative Short Text (typically 20 characters) that clearly identifies the WBS element. In the Description field, elaborate further on the specific tasks or deliverables encompassed by the element. Clear and consistent descriptions are vital for effective communication and understanding within the project team.
- WBSElement Category: SAP offers various WBS element categories for different project breakdown structures. These categories can help with filtering, reporting, and analysis later in the project lifecycle. Choose the most appropriate category based on your project’s needs (e.g., Investment, Internal Order, etc.).
Pro Tips for Effective WBS Creation
Now that you’ve grasped the basics of creating WBS elements in SAP, let’s delve deeper and explore some key strategies to ensure your WBS is not just functional, but truly effective in guiding your project to success.
1. Define Clear and Concise Descriptions for Each WBS Element
The description assigned to each WBS element serves a critical purpose. It should be a clear and concise statement that accurately reflects the work encompassed within that element.
- Strive for Clarity: Avoid ambiguity by using specific and actionable language. Instead of “Marketing Activities,” a more effective description might be “Develop and Execute Marketing Campaign for Product Launch.” This clarity ensures everyone involved understands the exact deliverables associated with each element.
- Maintain Consistency: Develop a consistent naming convention across your WBS. This will improve readability and make it easier for team members to navigate the project structure. For instance, consider using a numbering system or specific prefixes to categorize different types of activities within the WBS.
2. Utilize a Hierarchical Structure to Break Down Complex Projects
A well-defined hierarchical structure is the backbone of a strong WBS. By breaking down complex projects into manageable sub-elements, you gain a clearer picture of the overall workflow and establish a logical sequence for completing tasks.
- Start Broad, Refine Gradually: Begin by outlining the major project phases at the top level of your WBS. These could be phases like “Planning,” “Execution,” and “Closure.” Then, progressively decompose each phase into sub-elements representing specific tasks or deliverables. This step-by-step approach ensures a comprehensive and well-organized WBS.
- Balance Detail with Manageability: While a detailed WBS offers a granular view of the project, avoid creating an overly complex structure. Ideally, each WBS element should represent a manageable unit of work, typically estimated to take between 4 to 8 hours to complete. This level of granularity allows for accurate time and resource allocation during project planning.
FAQ about WBS Elements in SAP
Understanding how to work with WBS elements effectively goes beyond the initial creation process. Here, we’ll address some frequently asked questions to solidify your grasp on this valuable project management tool:
Can I create WBS elements in mass?
While SAP doesn’t offer a direct “mass creation” function for WBS elements like it does for some other data, there are ways to achieve a similar outcome for efficient project setup.
- Using the Copy Function: The PS module allows you to copy existing WBS elements. This is particularly useful when you have a similar project structure with minor variations. Simply select the existing WBS element, utilize the “Copy” function, and modify the details for the new element as needed.
- Considering Alternatives: For large-scale WBS creation, exploring advanced options like LSMW (Legacy System Migration Workbench) or custom ABAP programs might be necessary. These solutions involve data mapping and require technical expertise. Consulting with your IT team or an SAP specialist is recommended for such approaches.
Where can I view the WBS hierarchy in SAP?
Visualizing the breakdown of your project structure is crucial for effective communication and monitoring. SAP provides a dedicated tool for this purpose:
- Project Planning Application (CJ30): This user-friendly application allows you to navigate the WBS hierarchy graphically. You can expand and collapse elements, view details associated with each level, and gain a comprehensive understanding of your project’s scope.
- Benefits of Project Planning App: The Project Planning app goes beyond just displaying the structure. It allows you to drag and drop elements to adjust the hierarchy, filter for specific WBS components, and drill down into individual elements for further analysis. This interactive functionality empowers better project visualization and control.
What are the different types of WBS elements?
By understanding the various WBS element categories, you can tailor your project breakdown structure to best suit your needs:
- Task (T): This is the most common type of WBS element. It represents a specific activity or deliverable within the project. Tasks are typically planned in detail with assigned resources, durations, and costs.
- Project Definition (PR): This category serves as the starting point of your WBS. It represents the overall project and encompasses all subordinate WBS elements. There can only be one project definition element per project.
- Milestone (MS): Milestones signify key achievement points within the project that mark significant progress. They typically don’t involve resource allocation or cost planning but serve as crucial checkpoints for tracking project advancement.
- WBS Header (W): This category allows for grouping related tasks or sub-projects under a single header for better organization and overview. Header elements themselves don’t represent specific activities but act as containers for lower-level tasks within the project hierarchy.
Conclusion
By implementing WBS elements effectively in SAP, you’ve gained a powerful tool to conquer complex projects. You can now break down your project into manageable pieces, ensuring clarity, improved planning, and ultimately, project success. Remember, clear and concise WBS element descriptions paired with a well-defined hierarchical structure are foundational. Don’t hesitate to leverage WBS templates and link your WBS elements to activities and networks for a comprehensive plan. Finally, SAP offers functionalities to address situations where you need to create WBS elements in bulk.
So, take charge and start using WBS elements in SAP today! As a final tip, remember that a well-defined WBS is a living document. Don’t be afraid to revisit and update your WBS as your project progresses to reflect any changes or adjustments. With WBS elements by your side, you’ll be well on your way to achieving efficient and successful project management within SAP.
you may be interested in this blog here